This tutorial is created to illustrate the basic CRUD (Create , Read, Update, Delete) operation using SQL with Laravel 8. Laravel is one of the fastest-growing frameworks for PHP. Laravel 8 continues the improvements made in the previous stable release. Refer release notes to see the changes made in Laravel 8.
In this tutorial, You’ll learn to create the basic CRUD operations in Laravel. Follow the step-by-step guide to implement CRUD in Laravel 8.
What is CRUD?
When we are creating any dynamic web applications, it deals with some database operations such as Create, Read, Update, and Delete which are the four basic functions that we implement with the model. Hence, Software Engineers or Computer scientists often refer to these functions with the acronym CRUD .
- Install Laravel
First, let install Laravel using the following command (Make sure you have installed composer in your PC). Click on Install Composer If you haven’t installed Composer on your PC.
composer create-project --prefer-dist laravel/laravel stock_management
- Configure the Database
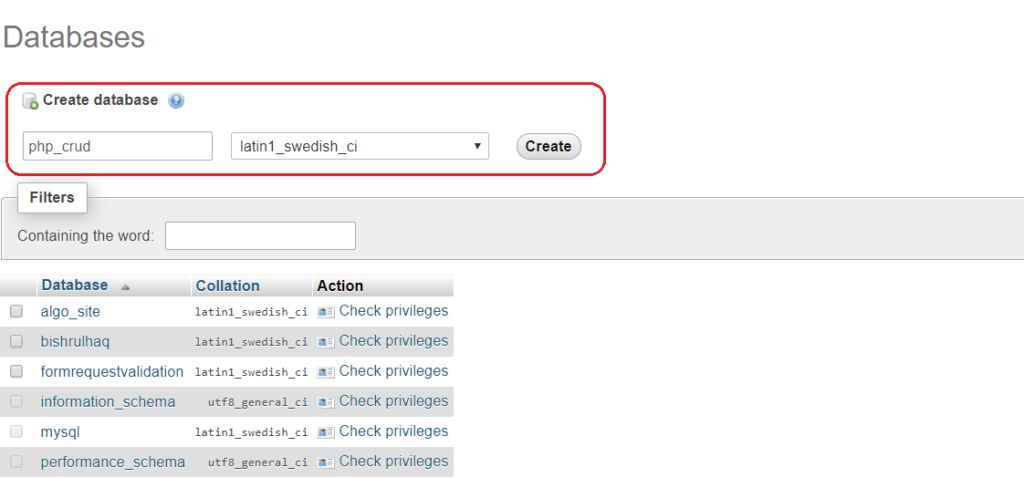
You need to create the database at MYSQL and then we need to connect that database to the Laravel project (You can also use phpmyadmin to create the database). Open the .env file inside Laravel project and add the database credentials as below.
.env
DB_CONNECTION=mysql
DB_HOST=127.0.0.1
DB_PORT=3306
DB_DATABASE='Your DB Name'
DB_USERNAME='Your DB UserName'
DB_PASSWORD='Your DB Password'
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)- Create the Stock Model and Migration
Next we are going to create the model using the following artisan command which will create the Model and the corresponding migration file.
php artisan make:model Stock -m
Code language: CSS (css)Open app/Models/Stock.php file and define the modal values in the $fillable prop.
app\Models\Stock.php
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Factories\HasFactory;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Stock extends Model
{
use HasFactory;
public $fillable = [
'product_name',
'product_desc',
'product_qty'
];
}
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)The migration will be created under “database/migrations“. Edit the file with the code below to create Stock Table.
database/migrations/timestamp_create_stocks_table.php
<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
class CreateStocksTable extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('stocks', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('product_name');
$table->text('product_desc');
$table->integer('product_qty');
$table->timestamps();
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('stocks');
}
}
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)Type the following command to run the migration.
php artisan migrate
- Create Seeder
Next we are going to add some dummy data to the stock table using laravel Seeder using the following artisan command.
php artisan make:seeder StockTableSeeder
Code language: CSS (css)All seeders generated will be placed in the database/seeders directory.
database\seeders\StockTableSeeder.php
<?php
namespace Database\Seeders;
use App\Models\Stock;
use Illuminate\Database\Seeder;
class StockTableSeeder extends Seeder
{
/**
* Run the database seeds.
*
* @return void
*/
public function run()
{
Stock::create([
'product_name' => 'Twinty Pencil',
'product_desc' => 'HB 5 Drawing Pencil',
'product_qty' => 100,
]);
}
}
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)So, we have added the columns product_name, product_desc, product_qty values that will be stored in the database. Run the following command to execute StockTableSeeder :
php artisan db:seed --class=StockTableSeeder
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)- Create Route and Resource Controller
Now, It’s time to create the logic for CRUD operations. We will use the Resource Controller to define the operations under the pre-defined methods within the Resource Controller. Run the following Artisan command to create the Stock resource controller.
php artisan make:controller StockController --resource
Code language: CSS (css)In this step, Go to routes->web.php file, add the following line of code to direct the routes to Stock Controller.
<?php
use App\Http\Controllers\StockController;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Route;
// Redirects to the Stock Resource Controller
Route::get('/', function () {
return redirect('/stocks');
});
Route::resource('stocks', StockController::class);
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)Add the following lines of codes in StockController to manipulate the basic CRUD operations.
app\Http\Controllers\StockController.php
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use App\Models\Stock;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
class StockController extends Controller
{
public function index()
{
$stocks = Stock::latest()->paginate(5);
return view('stocks.index',compact('stocks'))->with('i', (request()->input('page', 1) - 1) * 5);
}
public function create()
{
return view('stocks.create');
}
public function store(Request $request)
{
$request->validate([
'product_name' => 'required',
'product_desc' => 'required',
'product_qty' => 'required',
]);
Stock::create($request->all());
return redirect()->route('stocks.index')->with('success','Created Successfully.');
}
public function show(Stock $stock)
{
return view('stocks.show',compact('stock'));
}
public function edit(Stock $stock)
{
return view('stocks.edit',compact('stock'));
}
public function update(Request $request, Stock $stock)
{
$request->validate([
'product_name' => 'required',
'product_desc' => 'required',
'product_qty' => 'required',
]);
$stock->update($request->all());
return redirect()->route('stocks.index')->with('success','Updated Successfully.');
}
public function destroy(Stock $stock)
{
$stock->delete();
return redirect()->route('stocks.index')->with('success','Student deleted successfully.');
}
}
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)- Create the Views
Finally, create a folder Inside the resources\views directory as stocks within that folder, create the following five files.
- layout.blade.php
- index.blade.php
- create.blade.php
- edit.blade.php
- show.blade.php
layout.blade.php
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Laravel 8 CRUD Application - bishrulhaq.com</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.0.0/css/bootstrap.min.css" integrity="sha384-Gn5384xqQ1aoWXA+058RXPxPg6fy4IWvTNh0E263XmFcJlSAwiGgFAW/dAiS6JXm" crossorigin="anonymous">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="card" style="margin-top: 20px;">
<div class="card-body">
@yield('content')
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)index.blade.php
@extends('stocks.layout')
@section('content')
<div class="row">
<div class="col-lg-12">
<h2 class="text-center">Simple Stock Management Application | BH</h2>
</div>
<div class="col-lg-12 text-center" style="margin-top:10px;margin-bottom: 10px;">
<a class="btn btn-success " href="{{ route('stocks.create') }}"> Add Stock</a>
</div>
</div>
@if ($message = Session::get('success'))
<div class="alert alert-success">
{{ $message }}
</div>
@endif
@if(sizeof($stocks) > 0)
<table class="table table-bordered">
<tr>
<th>No</th>
<th>Product Name</th>
<th>Product Description</th>
<th>Qty.</th>
<th width="280px">More</th>
</tr>
@foreach ($stocks as $stock)
<tr>
<td>{{ ++$i }}</td>
<td>{{ $stock->product_name }}</td>
<td>{{ $stock->product_desc }}</td>
<td>{{ $stock->product_qty }}</td>
<td>
<form action="{{ route('stocks.destroy',$stock->id) }}" method="POST">
<a class="btn btn-info" href="{{ route('stocks.show',$stock->id) }}">Show</a>
<a class="btn btn-primary" href="{{ route('stocks.edit',$stock->id) }}">Edit</a>
@csrf
@method('DELETE')
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-danger">Delete</button>
</form>
</td>
</tr>
@endforeach
</table>
@else
<div class="alert alert-alert">Start Adding to the Database.</div>
@endif
{!! $stocks->links() !!}
@endsection
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)create.blade.php
@extends('stocks.layout')
@section('content')
<div class="row">
<div class="col-lg-12">
<h2 class="text-center">Add Stock</h2>
</div>
<div class="col-lg-12 text-center" style="margin-top:10px;margin-bottom: 10px;">
<a class="btn btn-primary" href="{{ route('stocks.index') }}"> Back</a>
</div>
</div>
@if ($errors->any())
<div class="alert alert-danger">
<strong>Oops!</strong> There were some problems with your input.<br><br>
<ul>
@foreach ($errors->all() as $error)
<li>{{ $error }}</li>
@endforeach
</ul>
</div>
@endif
<form action="{{ route('stocks.store') }}" method="POST">
@csrf
<div class="row">
<div class="col-xs-12 col-sm-12 col-md-12">
<div class="form-group">
<strong>Product Name:</strong>
<input type="text" name="product_name" class="form-control" placeholder="Product Name">
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-xs-12 col-sm-12 col-md-12">
<div class="form-group">
<strong>Product Description:</strong>
<textarea class="form-control" style="height:150px" name="product_desc" placeholder="Product Description"></textarea>
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-xs-12 col-sm-12 col-md-12">
<div class="form-group">
<strong>Qty:</strong>
<input type="number" class="form-control" name="product_qty" placeholder="Quantity">
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-xs-12 col-sm-12 col-md-12 text-center">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
@endsection
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)edit.blade.php
@extends('stocks.layout')
@section('content')
<div class="row">
<div class="col-lg-12">
<h2 class="text-center">Edit Stock</h2>
</div>
<div class="col-lg-12 text-center" style="margin-top:10px;margin-bottom: 10px;">
<a class="btn btn-primary" href="{{ route('stocks.index') }}"> Back</a>
</div>
</div>
@if ($errors->any())
<div class="alert alert-danger">
<strong>Whoops!</strong> There were some problems with your input.<br><br>
<ul>
@foreach ($errors->all() as $error)
<li>{{ $error }}</li>
@endforeach
</ul>
</div>
@endif
<form action="{{ route('stocks.update',$stock->id) }}" method="POST">
@csrf
@method('PUT')
<div class="row">
<div class="col-xs-12 col-sm-12 col-md-12">
<div class="form-group">
<strong>Product Name:</strong>
<input type="text" name="product_name" value="{{ $stock->product_name }}" class="form-control" placeholder="Product Name">
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-xs-12 col-sm-12 col-md-12">
<div class="form-group">
<strong>Product Description:</strong>
<textarea class="form-control" name="product_desc" style="height:150px" placeholder="Product Description">{{ $stock->product_desc }}</textarea>
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-xs-12 col-sm-12 col-md-12">
<div class="form-group">
<strong>Qty:</strong>
<input type="number" name="product_qty" class="form-control" style="height:150px" value="{{ $stock->product_qty }}" placeholder="Quantity">
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-xs-12 col-sm-12 col-md-12 text-center">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
@endsection
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)show.blade.php
@extends('stocks.layout')
@section('content')
<div class="row">
<div class="col-lg-12">
<h2 class="text-center">Show Stock</h2>
</div>
<div class="col-lg-12 text-center" style="margin-top:10px;margin-bottom: 10px;">
<a class="btn btn-primary" href="{{ route('stocks.index') }}"> Back</a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-xs-12 col-sm-12 col-md-12">
<div class="form-group">
<strong>Product Name : </strong>
{{ $stock->product_name }}
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-xs-12 col-sm-12 col-md-12">
<div class="form-group">
<strong>Product Description : </strong>
{{ $stock->product_desc }}
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-xs-12 col-sm-12 col-md-12">
<div class="form-group">
<strong>Quantity : </strong>
{{ $stock->product_qty }}
</div>
</div>
</div>
@endsection
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)Type the following command in your terminal to run the application.
php artisan serve
Hope this tutorial helps you! Feel free to drop your opinion at the comment section.